The Hough Transform is a method that is used in image processing to detect any shape, if that shape can be represented in mathematical form. It can detect the shape even if it is broken or distorted a little bit.
We will see how Hough transform works for line detection using the HoughLine transform method. To apply the Houghline method, first an edge detection of the specific image is desirable. For the edge detection technique go through the article Edge detection
Basics of Houghline Method
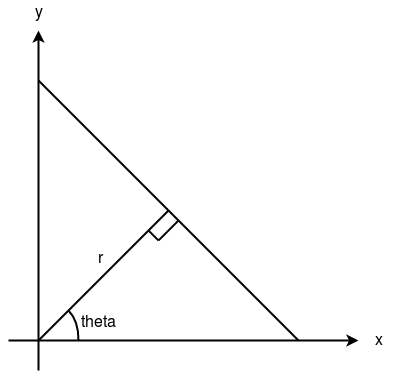
A line can be represented as y = mx + c or in parametric form, as r = xcos? + ysin? where r is the perpendicular distance from origin to the line, and ? is the angle formed by this perpendicular line and horizontal axis measured in counter-clockwise ( That direction varies on how you represent the coordinate system. This representation is used in OpenCV).

So Any line can be represented in these two terms, (r, ?).
Working of Houghline method:
Example:
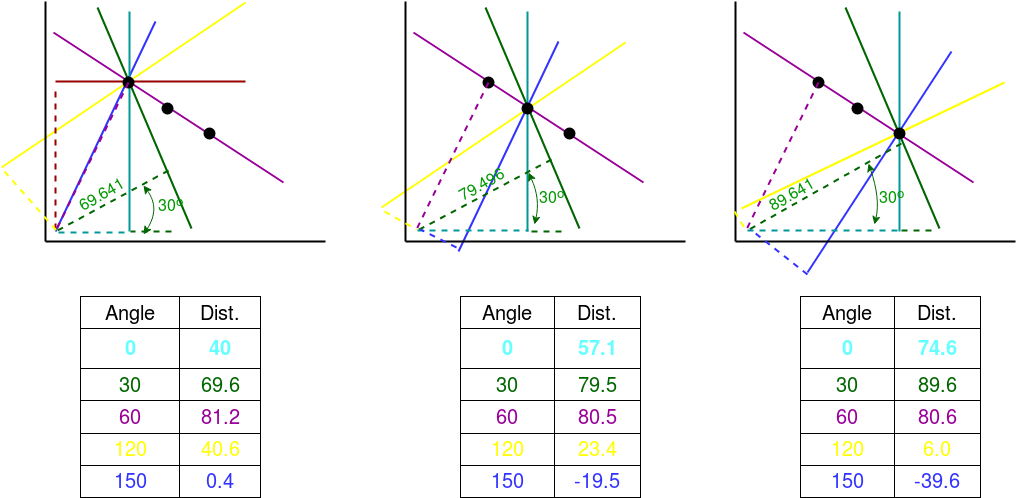
Consider a 100×100 image with a horizontal line at the middle. Take the first point of the line. You know its (x,y) values. Now in the line equation, put the values ?(theta) = 0,1,2,….,180 and check the r you get. For every (r, ?) pair, you increment value by one in the accumulator in its corresponding (r, ?) cells. So now in accumulator, the cell (50,90) = 1 along with some other cells.
Now take the second point on the line. Do the same as above. Increment the values in the cells corresponding to (r, ?) you got. This time, the cell (50,90) = 2. We are actually voting the (r, ?) values. You continue this process for every point on the line. At each point, the cell (50,90) will be incremented or voted up, while other cells may or may not be voted up. This way, at the end, the cell (50,90) will have maximum votes. So if you search the accumulator for maximum votes, you get the value (50,90) which says, there is a line in this image at distance 50 from origin and at angle 90 degrees.
Everything explained above is encapsulated in the OpenCV function, cv2.HoughLines(). It simply returns an array of (r, 0) values. r is measured in pixels and 0 is measured in radians.
Elaboration of function(cv2.HoughLines (edges,1,np.pi/180, 200)):

Alternate simpler method for directly extracting points:
Summarizing the process
Applications of Hough transform: